- Nature of the event
- Impact of the event
- Managment responses
Cast Studies
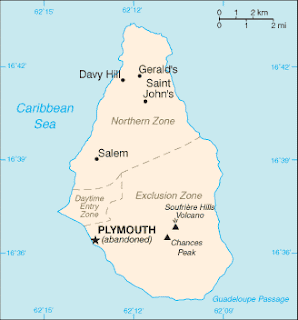
Montserrat - Volcanic LEDC
Nature of the Event
- Atlantic plate subducts beneath the Caribbean plate - destrictive plate boundary
- Island arc of composite volcanoes
- 16km long; 10km wide; made of volcanic rock
- Lava domes created due to andesitic lava
- As lava gets too heavy the dome collapses causing pyroclastic flows
- 18th July 1995 - youngest volcano erupts ash and dust
- Volcano was dormant
- 25th June 1997 "Chances Peak" volcano erupted 5 million cubic cm of hot rock and gases down the Soufriére Hills
- South of the Island covered by pyroclastic flows
- 11th February 2010 "Chances Peak" ejected 15km of ash
Impact of the Event
- Left rich volcanic soil
- 19 people killed due to fires
- Burn and inhalation injuries
- 2/3 houses buried by ash or flattened by rocks
- Farmland and vegetation destroyed along with 3/4 of infrastructure
- over half the 11,000 population evacuated (Antigua, USA, UK)
- Reconstruction of airports and docklands around capital Plymouth
- Fertile land was made unuseable
- Wildlife affected
- Ash plume spread to Antigua
Management of the Event
- Evacuation of the South half of the island
- April 1996 USA troops and UK Navy aided evacuation
- £17million UK emergency Aid e.g. water purification systems
- 3 year redevelopment programme funded by the UK
- Top-Heavy population pyramid (as young move away)
- Plymouth still remains an exclusion zone
- Vegetation is slowly re-growing
Mount Etna - Volcanic MEDC
Mount Etna - Sicily
- 1669 summit destroyed and lava reached the sea ove 10miles away
- Not so dangerous and thousands of people live on its slopes
- Fertile soil - perfect for farming as main source of income
- Eurasian Plate and African Plate causing subduction
Nature of the Event
- Violent explosions
- Basaltic lava flows
- Calderas on the volcano slopes
- Explosive, Strombolian eruptions
- Ash clouds (visible from space)
- Elongated lava domes (pahoehoe lava)
- Side vents on the side of volcano
- Pyroclastic flows
- Ash falls
- Mudflows
- Lava flows
- Crops destroyed
- Buildings destroyed and damaged
- Evacuation
- Minor earthquakes and tremors
- Damage to communications
- Smoke rings
- 1669 - "Operation Volcano Buster" US Marines blast a hole in the lava tunnel then dropped blocks of concrete into the hole to try and stem the flow - UNSUCCESSFUL IN 1669 + 1992
- 1992 - To save town of Zafferana - Earth barriers 234m long; 21m high, constructed to try and protect the area from lava flow to create a diversion channel - SUCCESSFUL
- 2/3 of lava was diverted but eventually the flow stopped 850km from Zafferana
- Diversion of the flow to uninhabited areas
- Low effusion rates
- High elevation of eruptive vents
Nature of the Event
- 12th January 2012
- 7 on the Richter scale
- Destructive plate margin - North American and Caribbean plates lateral movement past each other
- 52 aftershocks measuring over 4.5 on the Richter scale
- Focus 13km underground (shallow)
- Epicentre 25km from capital Port-au-Prince
Impacts of the Event
- 230,000 + deaths
- 2million people homeless in 60seconds
- Ground slumped
- Electricity lost
- 50% of buildings collapsed including Police HQ and Parliament
- Damage ot infrastructure
- Cracks in roads and debris blocking the road
- Ports and Airports closed
- Strong aftershocks
- Government was crippled so troops were looked for
- Prices of food increased so too expensive for most
- Looting and lawlessness due to lack of police
- Dead in the streets not removed = diseases e.g. cholera
- 1.5 million still homeless a year after the event
- Still lots to clear today
Management of the Event
- United Nations Development Project helped clear roads and debris
- US troops took over airport and ports
- UN troops were police and restored law and order
- UN World food programme provided basic food
- Water bottles distributed
- Emergency surgeries set up
- 591 make-shift camps
- Farmers encouraged towards self-sufficient so les reliance on imports
- Buildings made earthquake proof
Synoptic Links to Haiti Earthquake
- Chile earthquake: X10 richer than Haiti; educated about earthquakes; 8.8 Richter scale so stronger than Haiti but less deaths
- Planning, Prediction and Preparation
- Industry and economy
- Aid
- Aftershocks
L'Aquila Earthquake - Italy MEDC
Nature of the Event
- 6.3 Richter scale
- Eurasian and African Plate collision
- Fold mountains
- Focus 10km (shallow)
- 300 aftershocks
- Lasted 20 seconds
Impacts of the Event
- 300 died
- 58,000 homeless
- Buildings collapsed due to poor planning and destroyed
- Villages destroyed and damaged
- Civil unrest
- Looting
- $16 billion insurance claims due to having possesions
- 80,000 left unemployed
- 28,000 students left without access to university
- Estimated 2.4 billion euros economic cost
Management of the Event
- Good communications
- Emergency crews in scene immediately
- International aid arrived within 24hours
- Government had an emergency plan in place
- Hospitals prepared
- Buildings built with earthquake designs to earthquake resistane standards
- Berlisconi declared state of emergency
- 34,000 in temporary tents
- Red Cross provided meals
"If this earthquake had occured in California it wouldn't have killed one person"
Boxing Day Tsunami 2004
Nature of the Event
- Submarine earthquakes caused by tectonic activity
- Indo-Australian and Eurasian plates
- Epicentre: Banda Aceh
- Focus 30km below sea level
- 10 waves piled up on each other
- 24m high
- moving speed of 13.5m/second
Impact of the Event
- 250,000 died
- Thousands missing
- Villages and industried destroyed
- Drowing
- Loss of socio-economic groups
- Impact on tourism and residents
- Lack of communications so hard to direct the reconstruction
- International aid and Non-Governmental Organisations helped
- Roads blocked
- Farmladn destroyed
- Increased gap between rich and poor
- Drinking water contaminated
- Japan 2011 Tsnuami: had warning systems
- Waves surged inland up to 1km
- Technology beneficial in the recovery
- Food and water shortages
- 100,000 soldiers put in place to establish order and aid rescue work
- Over 700 aftershocks
- Exclusion zone set up due to Fucushmia nuclear power leaks




Some of the dates and spelling on these are shocking!
ReplyDelete